Understanding the Post-Pandemic World Economy
The world economy has been greatly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, with a significant decrease in global trade and economic activity. As businesses around the world attempt to return to normal operations, it is important to understand how the post-pandemic world economy will look and what steps can be taken to help rebuild economic growth. In this blog post, we will explore the effects of the pandemic on the world economy and discuss the strategies and policies that will help shape the future of the global economy.
The impact of the pandemic on the world economy
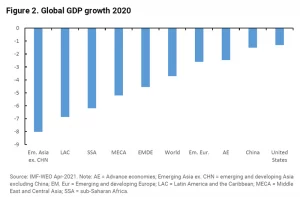
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought the global economy to a standstill, causing widespread disruptions across various sectors and industries. The pandemic has led to an unprecedented decline in economic activity, resulting in job losses, business closures, and significant damage to economies worldwide.
The pandemic’s impact on the world economy has been severe, with most countries experiencing a sharp decline in GDP and other key economic indicators. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing measures have severely affected many industries such as hospitality, aviation, tourism, and entertainment, resulting in massive job losses and business closures.
Furthermore, supply chains have been disrupted, causing shortages of critical products such as medical supplies and food. Governments worldwide have had to implement fiscal and monetary policies to mitigate the impact of the pandemic, resulting in significant increases in public debt and central bank balance sheets.
In short, the pandemic has resulted in a global economic recession, with significant implications for the future of the world economy. It has highlighted the need for greater global cooperation and has brought attention to the need for greater resilience and preparedness in the face of global crises.
Key changes in the global economy post-pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a major shock to the world economy, disrupting global supply chains, reducing demand for goods and services, and leading to widespread unemployment. As countries start to recover, there are several key changes that we can expect to see in the global economy.
One of the biggest changes is the shift towards digitalization and automation. The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of technology, as businesses have had to adapt to remote work and digital communication. This has led to increased investment in technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and e-commerce.
Another change is the emphasis on sustainability and resilience. The pandemic has highlighted the fragility of global supply chains, and businesses are now looking for ways to make their operations more resilient. This includes reducing dependence on single suppliers or countries, investing in local supply chains, and improving energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Consumer behavior has also changed, with people becoming more cautious and value-conscious in their spending. This has led to a shift away from luxury goods and services, and towards essential products such as groceries, healthcare, and home entertainment. Online shopping has also surged, as people avoid crowded stores and malls.
The labor market has also undergone major changes, with remote work becoming more widespread. This has led to a shift away from traditional office-based jobs, and towards more flexible and location-independent roles. The gig economy has also grown, with platforms like Uber and Airbnb providing opportunities for people to work and earn income on their own terms.
Governments have played a crucial role in shaping the recovery, with fiscal stimulus packages and monetary policies designed to support businesses and households. There has also been a growing recognition of the importance of public health, with increased investment in healthcare systems and research.
Global trade has been disrupted by the pandemic, with border closures and restrictions on travel and movement of goods. This has highlighted the need for more diversified and resilient supply chains, as well as increased cooperation and coordination between countries.
Finally, emerging markets are expected to play a key role in the post-pandemic recovery, as they offer opportunities for growth and investment. Countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are expected to benefit from growing demand for goods and services, as well as increasing investment in infrastructure and development.
Shifts in consumer behavior and their impact on businesses

The COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant changes in consumer behavior worldwide, and businesses must adapt to these changes if they want to remain competitive in the post-pandemic world economy.
One of the most significant shifts in consumer behavior has been the increased reliance on e-commerce. With lockdowns and social distancing measures in place, consumers have turned to online shopping in unprecedented numbers. As a result, businesses that have invested in their online presence and digital capabilities have been better equipped to weather the storm and thrive during the pandemic.
Another significant change has been in the way consumers prioritize health and safety. Consumers are more conscious than ever about the cleanliness and safety of the products they buy and the places they shop. Businesses that can demonstrate their commitment to health and safety through rigorous cleaning protocols, contactless payment options, and other measures will be more likely to earn the trust and loyalty of consumers.
The pandemic has also led to changes in spending habits, with consumers focusing on essentials and cutting back on non-essential purchases. Businesses that can offer essential goods and services at a competitive price will be better positioned to succeed in the post-pandemic world economy.
Lastly, the pandemic has also accelerated trends toward sustainability and ethical consumerism. Consumers are increasingly aware of the impact of their consumption habits on the environment and society. Businesses that can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and ethical practices will be more likely to attract and retain customers.
The role of technology in the post-pandemic world economy

The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies, fundamentally altering the way we live, work, and interact with one another. The unprecedented shift towards remote work, online education, telemedicine, and e-commerce has resulted in a surge in demand for technology products and services.
As a result, technology companies have emerged as winners in the pandemic era, with soaring stock prices and robust earnings growth. Big tech firms like Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Google, and Microsoft have experienced a surge in demand for their products and services, as well as increased adoption of their cloud-based platforms and remote collaboration tools.
The pandemic has also accelerated the growth of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies have played a vital role in mitigating the impact of the pandemic by facilitating remote monitoring, data analytics, and automation. The healthcare sector, for example, has seen a proliferation of digital health tools and wearables that enable patients to monitor their health remotely and receive real-time feedback from healthcare providers.
The adoption of technology has also resulted in the proliferation of new business models and industries. Online food delivery services, virtual events, and teleconferencing have all emerged as new industries with significant growth potential. Furthermore, technology has enabled the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi), which promises to revolutionize traditional finance by removing intermediaries and providing greater access to financial services.
However, the increased reliance on technology also raises concerns around cybersecurity, privacy, and job displacement. The pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of digital systems to cyberattacks, which can compromise critical infrastructure and cause significant economic damage. Moreover, the growth of automation and AI has raised concerns around job displacement and the need for upskilling and reskilling to keep up with the changing demands of the labor market.
Changes in the labor market and the rise of remote work

One of the most significant changes brought about by the pandemic is the shift towards remote work. With many countries imposing strict lockdowns and social distancing measures, businesses had to adapt to ensure the safety of their employees and maintain operations. As a result, remote work has become the norm for many industries.
The rise of remote work has implications for both employees and employers. On the one hand, it provides flexibility and convenience for workers who no longer have to commute to a physical office. This has led to a more balanced work-life balance and increased job satisfaction. On the other hand, remote work also means that employees may experience feelings of isolation and disconnectedness from their colleagues.
For employers, remote work offers the opportunity to reduce overhead costs associated with maintaining a physical office space. However, managing remote teams can present its own set of challenges, including maintaining team morale, communication, and productivity.
While the pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work, it remains to be seen how long this trend will last. Some experts predict that remote work will become a permanent feature of the labor market, while others argue that once the pandemic is over, workers will want to return to a physical office environment.
Nevertheless, the rise of remote work has the potential to impact the future of the labor market. It may lead to a decentralization of economic activity away from large urban centers and towards more remote locations. It may also increase opportunities for individuals who previously may not have had access to certain jobs due to geographical barriers.
As businesses continue to adapt to the changing landscape of work, it is important for governments and policy-makers to consider the potential implications and provide support where necessary. This includes ensuring access to high-quality internet connectivity, creating more flexible labor laws, and investing in skills training to prepare workers for the future of work.
The role of governments and policies in shaping the recovery
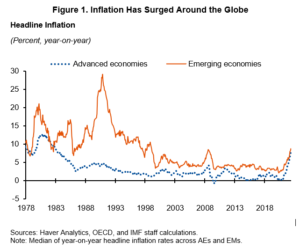
One of the most crucial factors in determining the shape and pace of the post-pandemic world economy will be the actions taken by governments and policymakers around the globe. The COVID-19 crisis has required unprecedented levels of government intervention, both in terms of public health responses and economic relief efforts.
In the short term, policymakers will need to focus on supporting struggling industries, protecting jobs, and providing stimulus to jumpstart economic activity. This could include measures such as fiscal stimulus, interest rate cuts, and expansionary monetary policies. Governments may also need to provide additional support for the most vulnerable populations, including low-income workers, small business owners, and the unemployed.
However, as the world economy continues to recover and adapt to the post-pandemic landscape, policymakers will need to consider longer-term strategies for fostering sustainable growth. This could include investing in infrastructure, promoting innovation and research and development, and addressing structural issues such as income inequality.
Additionally, policymakers will need to consider the potential impact of policies on global economic trends. For example, some countries may be tempted to pursue protectionist trade policies in response to the pandemic, which could lead to a more fragmented and isolated global economy. On the other hand, coordinated international efforts to support free trade and open markets could help to facilitate a more robust recovery.
Ultimately, the role of governments and policies in shaping the post-pandemic world economy will be multifaceted and complex. However, with a coordinated global response and a focus on sustainable growth, there is reason to be optimistic about the potential for a strong and resilient recovery.
Global trade and supply chain disruptions

The pandemic has caused widespread disruption to global trade and supply chains, with many businesses struggling to access the materials and goods they need to operate. Lockdowns, border closures, and quarantines have all had an impact on the movement of goods, leading to shortages of essential items such as medical supplies and raw materials.
One of the key factors driving supply chain disruptions has been the increasing reliance on just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing processes, which aim to minimize inventory and reduce costs. While JIT can be highly efficient in normal circumstances, it leaves companies vulnerable to disruption when unexpected events occur.
In addition to the disruption caused by the pandemic itself, there have been further challenges posed by trade tensions between major powers such as the United States and China. This has led to an increase in protectionist policies, including tariffs and export restrictions, which have further disrupted global supply chains.
The pandemic has highlighted the need for more resilient supply chains, with businesses seeking to diversify their suppliers and build greater redundancy into their operations. There has also been a renewed interest in domestic manufacturing and reshoring, as companies look to reduce their dependence on overseas suppliers.
Overall, the pandemic has underscored the interconnectedness of the global economy, and the importance of maintaining strong and resilient supply chains. Going forward, businesses and policymakers will need to work together to address the challenges posed by disruptions and build a more robust global trade system.
Emerging markets and their potential for growth
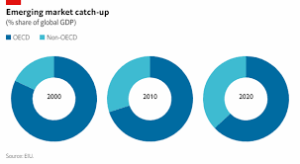
While the pandemic has had a profound impact on the global economy, it has also highlighted the potential for growth in emerging markets. These markets, which are characterized by rapid economic development and a growing middle class, have the potential to drive global economic growth in the years to come.
One of the main drivers of growth in emerging markets is the rise of digital technologies. As more people gain access to smartphones and the internet, businesses are able to reach new customers and create innovative products and services. This has created opportunities for startups and established companies alike, and has led to the creation of new jobs and industries.
Another factor contributing to the growth of emerging markets is the increasing importance of sustainability. As consumers become more conscious of the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions, businesses are responding by investing in green technologies and reducing their carbon footprint. This shift is particularly pronounced in emerging markets, where environmental degradation has often been a significant problem.
One of the most promising emerging markets is Africa, which has a young and rapidly growing population. As infrastructure improves and access to technology increases, African economies are poised to grow rapidly in the coming years. This growth presents significant opportunities for businesses looking to tap into new markets and expand their reach.
While emerging markets offer significant potential for growth, there are also significant risks to be aware of. These markets can be volatile, with political instability, currency fluctuations, and other factors impacting economic growth. Investors should be cautious and conduct thorough research before investing in these markets.
Overall, emerging markets offer significant potential for growth in the post-pandemic world economy. By investing in sustainable technologies and tapping into new markets, businesses can take advantage of these opportunities and contribute to global economic growth.
Implications for investors and investment opportunities
The pandemic has disrupted the global economy, but it has also created new investment opportunities for savvy investors. As economies recover, there will be a new set of winners and losers, and it will be important for investors to keep an eye on these changes. Here are some potential investment opportunities and considerations for investors in the post-pandemic world:
- Digital transformation: The pandemic has accelerated the shift towards digital technologies, and companies that are able to adapt and capitalize on this trend are likely to outperform. This could include companies involved in cloud computing, e-commerce, digital payments, and cybersecurity.
- Healthcare: The pandemic has highlighted the importance of healthcare systems, and companies that are involved in developing vaccines, treatments, and medical devices could be attractive investments. In addition, there may be increased demand for healthcare services in the coming years as populations age and chronic diseases become more prevalent.
- Emerging markets: Many emerging market economies have been hit hard by the pandemic, but they also offer potential for growth as they recover. Companies that are well-positioned in these markets, particularly in sectors such as technology and consumer goods, could be worth considering.
- ESG investing: The pandemic has highlighted the importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations for investors. Companies that prioritize sustainability, diversity, and ethical practices are likely to outperform over the long-term as investors increasingly factor these issues into their decision-making.
- Real estate: The pandemic has created disruption in the real estate market, particularly in commercial real estate. However, there may be opportunities in certain segments such as logistics and e-commerce infrastructure, as well as in the residential sector as people rethink their living arrangements.
Overall, the post-pandemic world economy presents a complex investment landscape. Investors will need to carefully consider the changing dynamics of the global economy, as well as their own risk tolerance and investment objectives. By keeping an eye on emerging trends and opportunities, investors can position themselves to succeed in the post-pandemic world.
